Welding is a process of joining two or more pieces of metal together by applying heat, pressure, or both. Welding can be done in various ways, such as using gas, electricity, lasers, or ultrasound. However, regardless of the welding method, one of the most important factors that affects the quality and efficiency of the weld is the welding position.
Welding position refers to the orientation of the weld joint relative to the horizontal and vertical planes. There are four basic welding positions: flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead. Each position has its advantages and disadvantages and requires different skills and techniques from the welder. In this article, we will explain the four basic welding positions and how to choose the right one for your project.
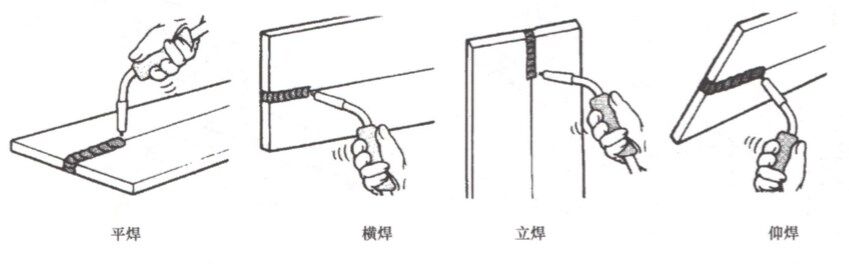
I. Flat Welding Position
The flat welding position is the easiest and most common welding position. It is also called 1G or down-hand position. In this position, the weld joint is placed on a horizontal plane and the welder works from above. The weld pool is supported by gravity, which makes it easier to control and prevents sagging or dripping. Flat position welding is suitable for most types of welds, such as fillet, groove, plug, or slot welds.

The flat position welding is ideal for beginners and for welding thin or light materials. It also allows for faster welding speed and a higher deposition rate. However, a flat position welding may not be suitable for welding thick or heavy materials, as it may cause excessive penetration or distortion. A flat position welding may also result in lower strength and toughness of the weld, as it does not provide enough stress relief.
II. Horizontal Welding Position
The horizontal welding position is also called 2G or the crosswise position. In this position, the weld joint is placed on a vertical plane, and the welder works from the side. The weld pool is partially supported by gravity, but it also tends to sag or roll down. A horizontal position welding requires more skill and technique from the welder than a flat position, as it involves balancing the heat input and travel speed to prevent undercutting or lack of fusion.

The horizontal position welding is suitable for welding pipes, tubes, or structural beams that cannot be rotated or moved. It can also be used for welding fillet or groove welds on plates or sheets that are too large or heavy to be placed in a flat position. A horizontal position can provide better strength and toughness than a flat position, as it provides more stress relief and reduces distortion.
III. Vertical Welding Position
Vertical welding position is also called 3G or upright position. In this position, the weld joint is placed on a vertical plane and the welder works from below (uphill) or above (downhill). The weld pool is not supported by gravity at all but rather pushed by the arc force. The vertical position requires more skill and technique from the welder than the horizontal position, as it involves controlling the arc length and electrode angle to prevent sagging or dropping.

The vertical position is suitable for welding pipes, tubes, or structural beams that cannot be rotated or moved horizontally. It can also be used for welding fillets or groove welds on plates or sheets that are too large or heavy to be placed in a horizontal position. A vertical position can provide better strength and toughness than a horizontal position, as it provides more stress relief and reduces distortion.
IV. Overhead Welding Position
The overhead welding position is also called 4G or overhead position. In this position, the weld joint is placed on a horizontal plane and the welder works from below. The weld pool is not supported by gravity at all but rather pulled by it. Overhead position requires more skill and technique from the welder than vertical position, as it involves controlling the heat input and travel speed to prevent falling or spattering.

The overhead position is suitable for welding pipes, tubes, or structural beams that cannot be rotated or moved vertically. It can also be used for welding fillet or groove welds on plates or sheets that are too large or heavy to be placed in a vertical position. Overhead position can provide better strength and toughness than vertical position, as it provides more stress relief and reduces distortion.
V. How to Choose the Right Welding Position for Your Project?
Choosing the right welding position for your project depends on several factors, such as:
The type of weld you want to make (fillet, groove, plug, etc.)
The shape and size of the base metal (plate, pipe, tube, etc.)
The thickness and weight of the base metal
The accessibility and visibility of the weld joint
The welding method and equipment you use (gas, electric, etc.)
The welding technique and skill you have (uphill, downhill, etc.)
The quality and efficiency you want to achieve
As a general rule, you should always choose the easiest and most comfortable welding position that can meet the requirements of your project. For example, if you want to weld a thin plate with a fillet weld, you should choose the flat position, as it is the easiest and fastest way to do it. However, if you want to weld a thick pipe with a groove weld, you may have to choose the vertical or overhead position, as it is the only way to access and cover the weld joint.
Another factor that can affect your choice of welding position is the type of welding procedure you use. Different types of welding procedures have different characteristics and requirements that may suit some positions better than others. For example, if you use aluminum welding techniques, such as TIG, MIG, or plasma arc welding, you may prefer the flat or horizontal position, as they allow for better control and penetration of the soft and thin metal. However, if you use other types of welding procedures, such as stick, flux-cored, or submerged arc welding, you may prefer the vertical or overhead position, as they allow for better deposition and coverage of the thick and heavy metal.
Ultimately, the best way to choose the right welding position for your project is to practice and experiment with different positions and see what works best for you. You should also consult with experienced welders or professionals who can give you advice and guidance on how to improve your welding skills and techniques.
I hope this article was helpful and informative for you. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to contact Megmeet Welding Technology.

Related article:
1. A Comprehensive Guide to Different Types of Welding Procedures
2. About Tungsten in TIG Welding: Types, Selection and Use
3. Welding Joint Types: Butt, Lap, Tee, Edge Joints & More.
4. 11 Types of Arc Welding: Applications & Benefits
5. Welding Porosity: Causes, Types, Effects and Solutions









